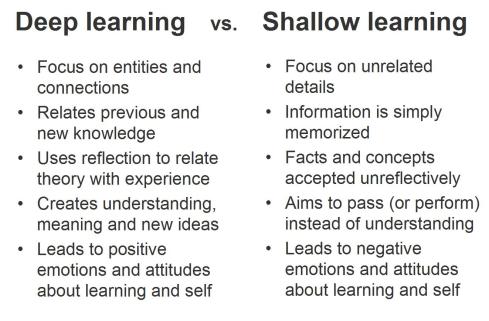
There are times when successful learning requires interactions between the student and the teacher/instructor. Often this is done in the form of feedback. As educators we should cherish these moments, because at best feedback is an opportunity to have an authentic dialogue with the student, which easily leads to a deeper learning experience. At the worst case scenario, receiving feedback makes the student think s/he was unfairly judged, which is an experience that may lead students to hate learning.
Feedback for deeper learning is information about students’ learning process and meeting the goal. In all levels of education feedback is an essential element in guiding students’ knowledge construction. Transparent feedback and assessment practices increase the quality of cognitive learning and help students to have better understanding their own learning process. According to APA, effective feedback must be clear, explanatory, and timely (2015, p. 12). Engaging in dialogue with students about feedback is an important – but often forgotten – part of of teaching-learning interactions. This dialogue is the magic ingredient that supports deep learning in all levels of education, from preK to higher education and professional development.
Feedback for deeper learning is not evaluation, assessment, labels, praise, or providing advice. Evaluation is a formal judgment about students’ work, often summative, and as such doesn’t function as feedback and supporting the learning process. Feedback is not assessment, either, because assessments focus on meeting competencies or goals/objectives, whereas feedback must focus on learning and guiding students to take action to meet the goals and build the competencies. Good and timely feedback enables students to “seek better strategies to complete the task” (Hattie & Timperley, 2007, p. 86). Grades, therefore, should never be considered to be feedback, because they are given after the learning is done, and there is nothing students can do to improve their learning.
Feedback is not about labeling students’ work with attributes like “good job”, “nice work”, “sloppy”, or “needs more” – weather in person or as written on students’ product (typically in the margin of an essay?). To enhance learning, feedback must be provided during the learning process, instead of only measuring the end result, the product (task, paper, project, etc.). Whether the label is positive (praise) or negative is irrelevant, because labels in education may have a detrimental effect of students’ academic self-concept and their self-efficacy. This is exactly why it is essential to have a strong informal feedback system to support the meaningfulness of learning and teaching. Bandura and Locke emphasize the importance of self-reflection and agency as a theory that by “embodying feed-forward self-regulation differs from control theories rooted solely in a negative feedback control system aimed at error correction” (2003, p. 87).
Feedback is an essential part of the learning process. Constructing learning environments and feedback around the fact that your students can affect their own learning helps them to become better learners for the rest of their lives. I cannot emphasize this enough! Regardless of the level of education, preK-12, college, university, workplace, or anything else, supportive feedback changes the way students think about their own learning process. Zimmerman call this “calibration” while talking about self-regulated learning (2013. p. 145). Both agency and self-regulation grow stronger with timely feedback, because it helps students to adjust their expectations and modify the plan to learn.
Giving effective feedback is not always easy. However, it is a skill that can (and should) be learned and taught. The basic principle in effective feedback is: Mistakes are a proof of trying. Acknowledging the positive in students’ attempts to learn gives the appropriate kind of feedback to keep students willing to try new things, and make new choices. Being afraid of making the wrong choice prevents students (or employees) from learning anything meaningful.
Moving away from labeling students or their skills, and starting to point out the progress they show in their learning process is a great way to start changing the feedback practices and emphasize deeper learning. Non-punitive assessment system is a requirement for feedback to support deeper learning.
The first step is to have a clear idea of the most important target for the feedback and an understanding of the desired outcome of the dialogue. Using open ended questions to get students’ input on how they see their own progress helps to figure out where and why they may struggle. Sometimes just inquiring about the next steps the student is planning to take and verbally situating those into the bigger picture of their learning experience or task completion is enough. When students are thinking about their own learning plan they are already engaging in deeper learning.
Please remember: only those mistakes that are allowed to be corrected can help students to learn more!
American Psychological Association, Coalition for Psychology in Schools and Education. (2015). Top 20 principles from psychology for pre K–12 teaching and learning. Retrieved from http:// http://www.apa.org/ed/schools/cpse/top-twenty-principles.pdf
Bandura, A., & Locke, E. A. (2003). Negative self-efficacy and goal effects revisited. Journal of applied psychology, 88(1), 87.
Hattie, J., & Timperley, H. (2007). The power of feedback. Review of educational research, 77(1), 81-112.
Zimmerman, B. J. (2013). From cognitive modeling to self-regulation: A social cognitive career path. Educational psychologist, 48(3), 135-147. Available at researchgate.